Notation in probability and statistics
Probability theory and statistics has some commonly used conventions of its own, in addition to standard mathematical notation and mathematical symbols.
Contents |
Probability theory
- Random variables are usually written in upper case roman letters: X, Y, etc.
- Particular realizations of a random variable are written in corresponding lower case letters. For example x1, x2, …, xn could be a sample corresponding to the random variable X.
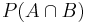 or
or ![P[A \cap B]](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/a1d773d1ed4a606353c3977b57e19317.png) indicates the probability that events A and B both occur.
indicates the probability that events A and B both occur.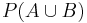 or
or ![P[A \cup B]](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/e4f296a87555c54f2f75cf1bd060f557.png) indicates the probability of either event A or event B occurring ("or" in this case means one or the other or both).
indicates the probability of either event A or event B occurring ("or" in this case means one or the other or both).- σ-algebras are usually written with upper case calligraphic (e.g.
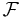 for the set of sets on which we define the probability P)
for the set of sets on which we define the probability P) - Probability density functions (pdfs) and probability mass functions are denoted by lower case letters, e.g. f(x).
- Cumulative distribution functions (cdfs) are denoted by upper case letters, e.g. F(x).
- In particular, the pdf of the standard normal distribution is denoted by φ(z), and its cdf by Φ(z).
- Some common operators:
-
- E[X] : expected value of X
- var[X] : variance of X
- cov[X, Y] : covariance of X and Y
Statistics
- Greek letters (e.g. θ, β) are commonly used to denote unknown parameters (population parameters).
- An estimate of a parameter is often denoted by placing a caret over the corresponding symbol, e.g.
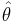 , pronounced "theta hat".
, pronounced "theta hat". - Some commonly used symbols for sample statistics are given below:
- the sample mean
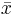 ,
, - the sample variance s2,
- the sample correlation coefficient r,
- the sample cumulants kr.
- the sample mean
- Some commonly used symbols for population parameters are given below:
- the population mean μ,
- the population variance σ2,
- the population correlation ρ,
- the population cumulants κr.
- The arithmetic mean of a set of numbers x1, x2, ..., xn is denoted by
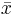 , pronounced "x bar".
, pronounced "x bar".
Critical values
The α-level upper critical value of a probability distribution is the value exceeded with probability α, that is, the value xα such that F(xα) = 1 − α where F is the cumulative distribution function. There are standard notations for the upper critical values of some commonly used distributions in statistics:
- zα or z(α) for the Standard normal distribution
- tα,ν or t(α,ν) for the t-distribution with ν degrees of freedom
 or
or  for the chi-squared distribution with ν degrees of freedom
for the chi-squared distribution with ν degrees of freedom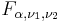 or F(α,ν1,ν2) for the F-distribution with ν1 and ν2 degrees of freedom
or F(α,ν1,ν2) for the F-distribution with ν1 and ν2 degrees of freedom
Linear algebra
- Matrices are usually denoted by boldface capital letters, e.g. A.
- Column vectors are usually denoted by boldface lower case letters, e.g. x.
- The transpose operator is denoted by either a superscript T (e.g. AT) or a prime symbol (e.g. A′).
- A row vector is written as the transpose of a column vector, e.g. xT or x′.
Abbreviations
Common abbreviations include:
- a.e. almost everywhere
- a.s. almost surely
- cdf cumulative distribution function
- cmf cumulative mass function
- df degrees of freedom (also
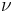 )
) - i.i.d. independent and identically distributed
- pdf probability density function
- pmf probability mass function
- r.v. random variable
- w.p. with probability; wp1 with probability 1
See also
- Glossary of probability and statistics
- Combinations and permutations
- Typographical conventions in mathematical formulae
- History of mathematical notation
References
- Halperin, Max; Hartley, H. O.; Hoel, P. G. (1965), "Recommended Standards for Statistical Symbols and Notation. COPSS Committee on Symbols and Notation", The American Statistician 19 (3): 12–14, doi:10.2307/2681417, JSTOR 2681417
External links
- Earliest Uses of Symbols in Probability and Statistics, maintained by Jeff Miller.